http://webaim.org/articles/cognitive/
Cognitive Disabilities
Introduction
Functional vs. Clinical Cognitive Disabilities
There are at least two ways to classify cognitive disabilities: by functional disability or by clinical disability. Clinical diagnoses of cognitive disabilities include autism, Down Syndrome, traumatic brain injury (TBI), and even dementia. Less severe cognitive conditions include attention deficit disorder (ADD), dyslexia (difficulty reading), dyscalculia (difficulty with math), and learning disabilities in general. Clinical diagnoses may be useful from a medical perspective for treatment, but for the purposes of web accessibility, classifying cognitive disabilities by
functional disability is more useful. Functional disabilities ignore the medical or behavioral causes of the disability and instead focus on the resulting abilities and challenges. Some of the main categories of functional cognitive disabilities include deficits or difficulties with:
- Memory
- Problem-solving
- Attention
- Reading, linguistic, and verbal comprehension
- Math comprehension
- Visual comprehension
The main reason why these functional disabilities are more useful when considering web accessibility is that they are more directly related to the concerns of Web developers. Telling a developer that some people have autism is not very meaningful unless the developer knows what kinds of barriers a person with autism might face. On the other hand, telling a developer that some people have difficulties comprehending math provides the developer with a framework for addressing this type of audience.
Additionally, clinical diagnoses are not mutually exclusive in terms of what difficulties the people face. There is often considerable overlap of functional disabilities within clinical diagnoses. A person with memory deficits may also have difficulty with attention or problem-solving, for example. This kind of overlap fits within a medical model, but is not particularly helpful to web developers, who simply need to know what the person can or cannot do.
Memory
Memory refers to the ability of a user to recall what they have learned over time. A common model for explaining memory involves the concepts of working (i.e., immediate) memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Meaningful information is typically moved up the chain from immediate to short-term into long-term memory stores. Some individuals with cognitive disabilities have difficulties with one, two, or all three of these memory types. The more meaningful content is to the needs of the user, the greater the chances that it will be moved into functional memory storage in the brain. Some users may have memory difficulties that impair their ability to remember how they got to content on and off the Web site.
Problem-Solving
Some individuals with cognitive disabilities have a difficult time solving problems as they arise. In many instances, their resilience can be low and the resulting frustration is such that they choose to leave the site and not persist to solve the problem. One example of this would be the presence of a 404 error from a bad link, or a link that does not take them where they thought they were going.
Attention

There are many individuals that have difficulty with focusing their attention to the task at hand. Distractions such as scrolling text and blinking icons can make the web environment difficult. Even for typical users the presence of blinking and scrolling items or multiple pop-ups can be irritating. Good design principles would limit these instances to only that which is necessary to convey the content.
Some people with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (
ADHD) have difficulties learning, but oftentimes this is due to their distractibility, rather than to any kind of inability to process information. People with
ADHD can be impulsive, easily distracted, and inattentive. On a positive note, some people with attention deficits are highly creative and very productive in short bursts, with an abundance of energy and enthusiasm. On a less positive note, it can be difficult for people with
ADHD to stick to a task for a long period of time. On the Web, flashing banner ads can be distracting, as well as anything that draws a person's attention away from the main content.
Reading, Linguistic, and Verbal Comprehension

Some individuals have difficulties understanding text. These difficulties may be mild or severe, ranging from minor challenges to a complete inability to read any text. It would be unreasonable to expect web developers to accommodate the entire range of reading abilities. The difference between non-readers and genius readers is simply too vast. It
is reasonable, however, to expect developers to write as simply and clearly as possible, taking into account the primary audience and including those who may have difficulty with some of the content. After all, an estimated 15-20% of the population has some sort of language or text comprehension difficulty.
Although the claims are difficult to verify, it is commonly reported that many famous leaders and intellectuals had difficulty reading and/or spelling, including: Winston Churchill, Thomas Edison, Henry Ford, Albert Einstein, George Washington, John F. Kennedy, Leonardo da Vinci and others. The take-home message is that writers do not know whether members of their audience have reading difficulties or not. This is a condition which many people manage to keep well hidden.
Here is one example of a reading problem. Note that it may be one of perception or of processing. See if the associated accessibility fix helps you.
What is being said in this phrase?
Tob eornot obe
Now check the power and importance of embedded graphics as a way to enhance the context of the written word by looking at the
phrase with a graphic.
Another interesting simulation of a reading difficulty and our resilience in the face of reading problems can be found at
http://www.angmail.fsnet.co.uk/jumbltxt.htm - external link.
Non-Literal Text
A problem for some readers is non-literal text, such as sarcasm, satire, parody, allegory, metaphor, slang, and colloquialisms. In some cases, readers will not realize that the words are not meant to be understood literally. A writer who says "I just love getting stuck in traffic when I'm already late for work" probably means the opposite of what this sentence actually says. Sarcasm such as this can be confusing to some readers. Similarly, someone who reads she must "get her ducks in a row" may not realize that the author is probably not referring to real ducks at all. The author is suggesting that the reader get organized or disciplined, using the comparison of a mother duck with her ducklings lined up behind her in order to illustrate the concept.
Non-Existent Text
The unstated assumptions and implied meaning of written content may seem obvious to the writer, but readers may not have the necessary background knowledge. Some readers may not have the skills to infer meaning from text without additional help.
Math Comprehension
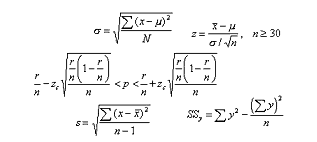
Mathematical expressions are not easy for everybody to understand. This does not mean that authors should avoid math entirely. For people who are comfortable reading equations and thinking mathematically, the best way to explain mathematical concepts is to use equations. On the other hand, often it is helpful to explain math conceptually, either with or without the formulas. Conceptual explanations help readers understand the reasoning behind the math.
Visual Comprehension
Some individuals have difficulties processing visual information. In many ways, this is the opposite of the problem experienced by people with reading and verbal processing difficulties. Individuals with visual comprehension difficulties may not recognize objects for what they are. They may recognize the fact that there are objects on a Web page, but may not be able to identify the objects. For example, they may not realize that a photograph of a person is a representation of a person, though they can plainly see the photograph itself (as an object) on the web page.
For these people, a moving, talking person in a video may be easier to identify and mentally process than a static image of a person in a photograph. Video and multimedia, accompanied with narration, may be the best way to communicate to these individuals.
Overview
Any list of design considerations for users with cognitive disabilities can easily turn into a lengthy list of usability concerns and general "good design principles." The ideas presented here do not exhaust all avenues of thought on the topic, by any means. They merely present some of the larger principles which categorize more specific techniques.
Accommodating Memory Deficits
Any kind of reminder of the overall context of a web site can help people with memory deficits. Lengthy interactive processes, such as those required to purchase items online, should be kept as simple and brief as possible. To focus the users' attention on specific tasks, the interaction should probably be broken up into separate pages, but help users keep track of their progress so they do not get lost in the process. Simple reminders such as "step 2 of 4" help them keep track of what they have already done and what they have left to do. Each step can also be named or labeled so instead of saying "previous page" and "next page," a link could say "previous page (payment and shipping information)" and "next page (review order)."
Accommodating Problem-Solving Deficits
Everyone at some point or another accidentally clicks on the wrong link, misspells a word, or commits some kind of error on the web. This is normal human behavior. In some individuals, this tendency is exaggerated, so they make even more mistakes. Whether people make many or few mistakes, everyone likes to be able to correct their errors. Error messages should be as explanatory as possible, telling users what they did wrong and how to fix the problem. Search features should suggest alternate spellings to users if the original spelling seems suspicious or if it returns no results. Users should be warned when actions can cause potentially serious consequences, such as deleting a file. In many cases, providing instructions at the start of a task will eliminate or at least reduce the overall number of user errors. Also, avoid extreme changes in the context of the web site without first warning users. All functionality should be as predictable as possible, and any deviations from predictability should be preceded by warnings and/or explained to users after the changes occur.
Accommodating Attention Deficits
Focus the attention of users. Use visual cues to highlight important points or sections of the content. If possible, eliminate advertisements and sponsored links. Use headings to draw attention to the important points and outline of the content. Avoid background noises or images that distract. Use them instead to focus the users attention.
Accommodating Reading, Linguistic, and Verbal Comprehension Deficits
Supplemental media
Supplemental media such as illustrations, icons, video and audio have the potential to greatly enhance the accessibility of web content for people with cognitive disabilities. The problem is that high quality media is often difficult to produce. Poor quality media may actually decrease the accessibility of Web content, by making it more confusing. But don't use this as an excuse not to try. Use your judgment. Incorporate media where it makes sense. Realize, too, that the vast majority of web content could benefit from some sort of supplemental media, if only supplemental graphics.
Document organization and structure
Structural organization
As a general statement, the more structured your document is, the easier it will be to understand. Structure in documents can be created by adding:
- headings
- bulleted lists
- numbered lists
- definition lists
- indented quotes (using the
<blockquote> tag)
All of the above structural elements can be added into the markup of the document. In other words, there are built in methods in
HTML of designating a part of your content as a heading, or a list item, etc.
Visual organization
You can also add visual structure to a document that will benefit those who have sight. For example, you can:
- indent sub-items in a hierarchical list*
- highlight items by changing the font color or background color
NOTE:
Developers should not ignore the semantics of the markup language when trying to achieve a visual effect. For example, despite the fact that the
<blockquote> tag causes the text within it to be visually indented, this tag should not be used for its visual effect alone. If the text truly is a quote, then the
<blockquote> tag is appropriate. If the text is not a quote, then
CSS (Cascading Style Sheet) attributes should be used to achieve the effect (for example, the developer could add the following style attribute to the paragraph tag:
style="margin-left: 5%").
White space
It is usually easier to read text when it is visually separated from the borders of the surrounding design. People with reading disorders, such as dyslexia, can benefit from white space in the margins and vertical white space between headings, paragraphs, tables, etc. Long paragraphs can be more difficult to read than shorter ones, partly because readers may lose their place within the paragraph.
Clear and simple writing
Short, simple, unambiguous phrases are easier to understand than long, complex, ambiguous ones. People with more profound cognitive disabilities need sentences that are extremely short, simple, and unambiguous. In some cases, they will not be able to understand sentences at all, relying completely on graphics, illustrations, and other non-text visual materials. This does NOT mean that you have to create image-only sites for general audiences, though adding high-quality supplemental illustrations is certainly a good idea. If, however, your primary audience is individuals with more severe cognitive disabilities you may need to create an image-only site.
To the extent possible, try to avoid non-literal content such as sarcasm, parody, and metaphors. Also make sure to give readers all necessary background information about the topic at hand.
(See also the section on writing clearly and simply.)
Accommodating Math Comprehension Deficits
Math computations or formulas can be difficult for many people to understand, whether they have a genuine deficit in math comprehension abilities or just "math phobia," to use the term "phobia" loosely. In this context, math phobia is not a clinical condition but a simple dislike of math, influenced largely by cultural factors. The United States, for some reason, has created a culture in which math is commonly disliked and derided. By way of comparison, math abilities are highly prized in Asian countries, and it would be somewhat of an insult to say that an Asian person is not good at math.
No matter what the cause of math comprehension deficits—biologically-based deficits or culturally-based aversions—authors can increase the understandability of their content by either avoiding math altogether, or by explaining the math conceptually. Where computations are required—as in e-commerce sites that add the price of the items purchased, tax, shipping and handling, and other charges—it is usually best to perform these computations automatically, so the user does not have to.
Accommodating Visual Comprehension Deficits
Usually, the best advice to help users with cognitive disabilities is to provide information in muliple formats, with a heavy emphasis on visual formats. While this remains true for the majority of people with cognitive disabilities, some types of cognitive disabilities cause difficulties in visual comprehension. If authors rely entirely on visual communication methods, some users will not understand the message. Visual communication methods include color, spatial relationships, styles, design elements, photos, images, etc.
Even though most web content suffers for a lack of visually-enhanced communicative methods, the take-home message is that no one method is sufficient by itself. Supplement the information with multiple modes and methods of communication.